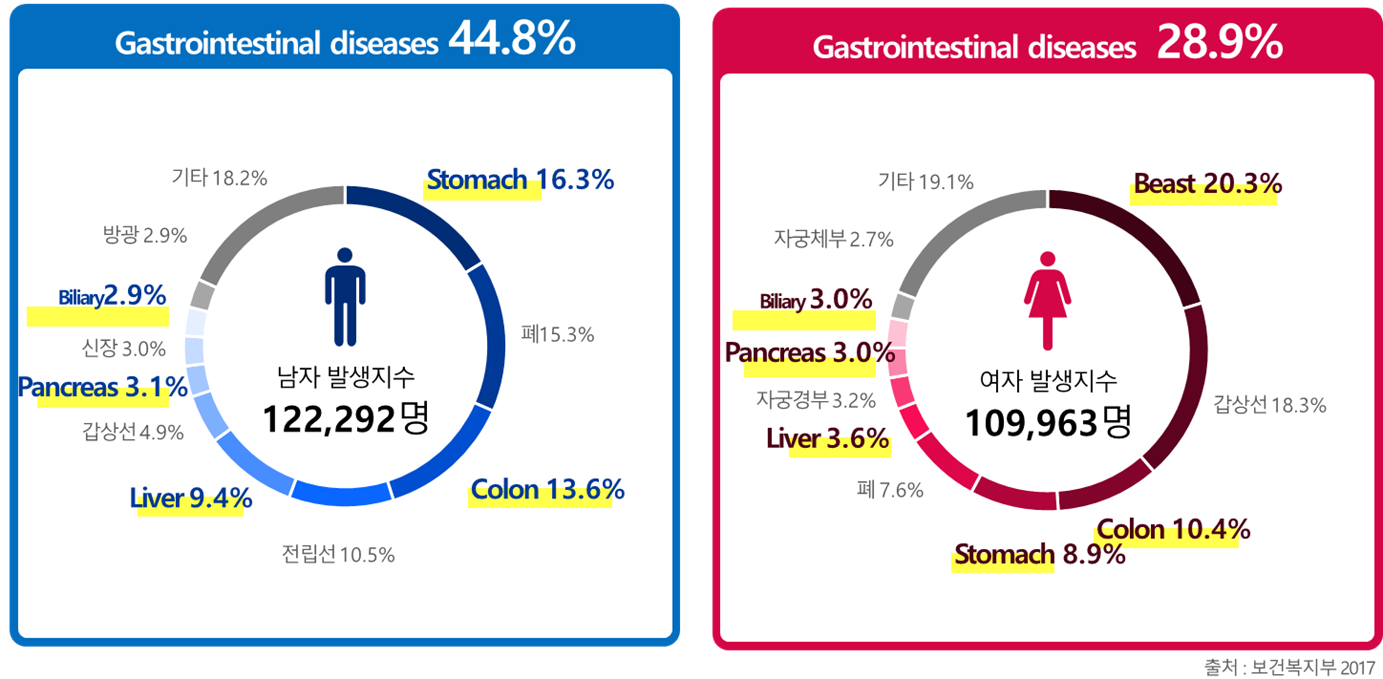
Rising Gastrointestinal Disease
Liver and digestive diseases occur frequently in Northeast Asia, including Korea, and the death rate has increased, and the resulting economic loss is also a disease (Figure). Accumulation of research capabilities is required for digestive diseases.
Effects and Expectations of Basic Research on Gastrointestinal Diseases
The knowledge accumulated through life science and basic research of digestive diseases is widely applied to clinical applications of medicine, and it is expected to contribute to innovation in translational research and personalized medicine, economic and industrial development, and promotion of human health and welfare.

In particular, the study of the intestinal microbiome, which is considered the second organ in the world, has been actively conducted recently, and the relationship between digestive diseases and the intestinal microbiome is being highlighted (Figure).
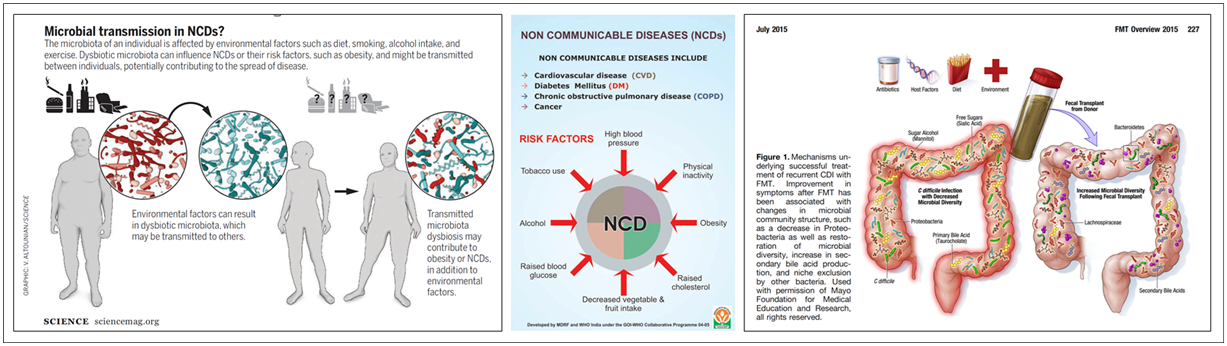
Methods to prevent or treat diseases by manipulating the gut microbiome are emerging as new treatments that are likely to expand to diseases including NCD and are emerging as a treatment that changes the medical paradigm. Fecal Microbiota Transplantation, a representative method for treating diseases by manipulating intestinal microbes, has been internationally established and revised guidelines.


